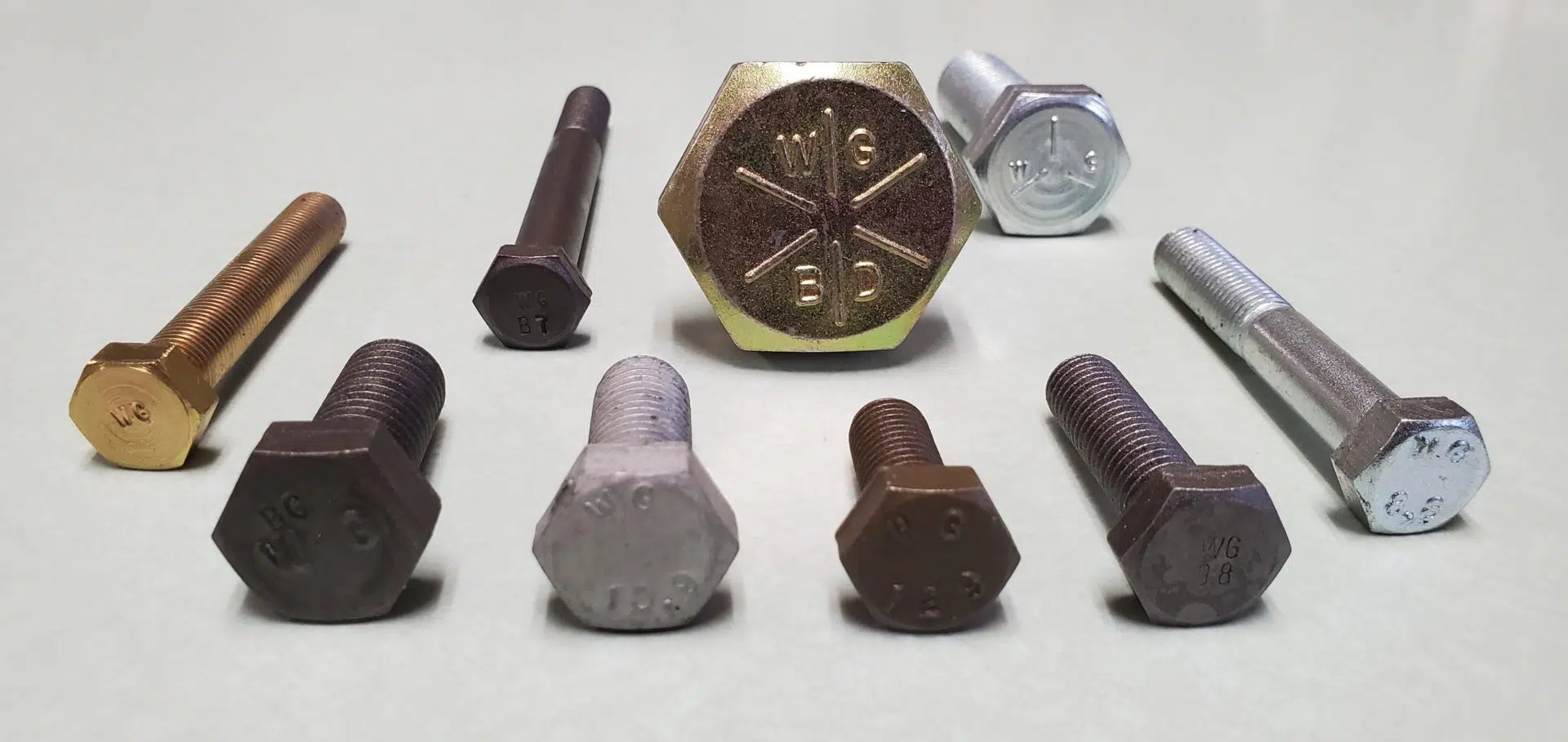
Understanding a Few Common ASTM Inch-Series Bolt Grade Markings
While SAE J429 Grades 2, 5, and 8 are probably the most common inch-series fastener specifications that we deal with here at Wilson-Garner, there are plenty of other ones with their own grades and head markings.
In this article, we’ll take a look at three standards from ASTM:
1. ASTM A307 Bolt Grade Markings
2. ASTM A193 Bolt Grade Markings
3. ASTM A354 Bolt Grade Markings
What Are ASTM Fastener Standards?
ASTM stands for the American Society for Testing and Materials. This organization has established various standards and specifications for fasteners like bolts and studs. Each of these standards introduces different grading systems based on letters, numbers, and combinations of both — think A, B, BC, B7, etc. These grades generally determine different tensile strengths.
Examples of ASTM Bolt Grade Markings
So, now let’s put this information together and discuss what some of the different ASTM fastener standards have to say about bolt grade head markings.
ASTM A307 Bolt Grade Markings
ASTM A307 Carbon Steel Bolts and Studs, 60,000 Psi Tensile Strength is a specification that creates three grades of bolts and studs: Grade A, Grade B, and Grade C — but Grade C has been replaced by a different standard, so we’ll ignore it here. ASTM A307 covers diameters ¼” to 4”. The grades are again differentiated by tensile strength, although the spec also differentiates by intended use.
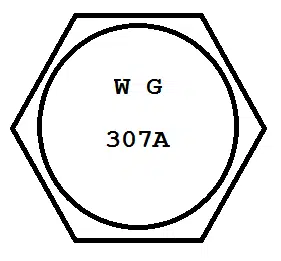
ASTM A307 Grade A
Here’s what an ASTM A307 Grade A bolt head marking would look like:
Grade A bolts and studs have a minimum tensile strength of 60 ksi and are intended for general applications. If you’re like us and have trouble remembering numbers, you’ll appreciate this head marking, because it includes the number of the spec.
Grade A bolts and studs are considered to be low-strength, having a tensile strength roughly equivalent to SAE J429 Grade 2. It’s generally not necessary to heat treat Grade A parts in order to meet the minimum tensile requirements.
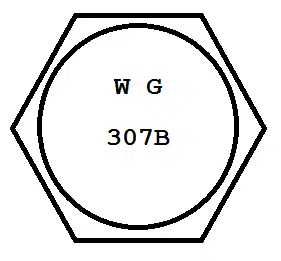
ASTM A307 Grade B
The head marking for a Grade B bolt can be seen here:
Yep, this is pretty much what we expected. Once again, the number of the spec is right there on the head if you need it, which is nice.
Grade B bolts and studs have a tensile strength between 60 ksi and 100 ksi. Their intended use is in flanged joints in piping systems with cast iron flanges. The major difference between Grade B and Grade A is that Grade B has minimum and maximum tensile strength requirements set by the spec, while Grade A only has a minimum tensile strength requirement.
ASTM A193 Bolt Grade Markings
ASTM A193 Alloy Steel and Stainless Steel Bolting for High-Temperature or High-Pressure Service and Other Special Purpose Applications is a specification that creates a rather large number of grades for inch-series bolts, screws, and studs up to seven inches in diameter.
As the title would lead you to believe, this spec deals with fasteners intended for use in high-temperature or high-pressure environments. It provides guidelines for six grades for parts made of ferritic (carbon or alloy) steels and more than twenty grades for parts made of austenitic stainless steels. There’s also a version of the standard, ASTM A193M, which lays out guidelines for metric-series fasteners.
But for the sake of brevity, let’s just take a look at the most common ASTM bolt grade that Wilson-Garner manufactures: Grade B7.
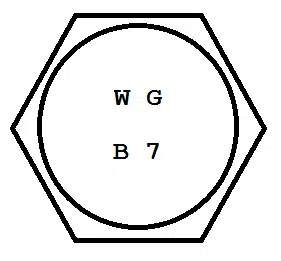
ASTM A193 Grade B7
Grade B7 bolts are made from alloy steel. While there’s a metric version of Grade B7 that can be found in ASTM A193M, we’re sticking to the inch-series version here.
Here we see the grade stamped into the bolt head marking. You may have noticed that this standard requires only the grade to be marked, while the previous standard we covered, ASTM A307, required the number of the standard along with the grade. The more you look at these things, the more you’ll notice that each standard, even standards written by the same organizations, tend to handle head markings a little differently.
Grade B7 bolts have a minimum tensile strength of 125 ksi for diameters 2 ½” and under, 115 ksi for diameters over 2 ½” through 4”, and 100 ksi for diameters over 4” through 7”. These minimum tensile strengths are roughly equivalent to the requirements for SAE J429 Grade 5. Therefore, these parts are considered to be medium-strength. Grade B7 parts are required to be heat-treated, quenched, and tempered.
ASTM A354 Bolt Grade Markings
ASTM A354 Quenched and Tempered Alloy Steel Bolts, Studs, and Other Externally Threaded Fasteners is a specification that lays out the guidelines for two grades: Grade BC and Grade BD. All parts in this standard must be made from alloy steel and be heat-treated, quenched, and tempered. This spec covers parts up to 4” in diameter.
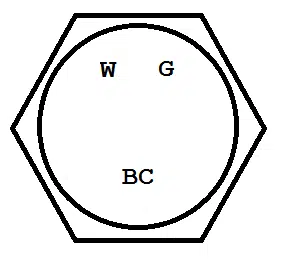
ASTM A354 Grade BC
Let’s take a look at the bolt head marking for Grade BC:
Again, we simply have the grade itself marked. Grade BC fasteners have a minimum tensile strength of 125 ksi for diameters ¼” through 2 ½”. The minimum tensile strength is 115 ksi for diameters over 2 ½” inches. Generally, Grade BC parts are considered to be medium-strength fasteners.
ASTM A354 Grade BD
The bolt head marking for Grade BD is shown here:
No surprises here. Grade BD parts have a minimum tensile strength of 150 ksi for diameters ¼” through 2 ½” and 140 ksi for diameters over 2 ½”. Grade BD parts are considered to be high-strength. The mechanical properties of Grade BD fasteners in diameters ¼” through 2 ½” are almost identical to those of SAE J429 Grade 8 — so similar, in fact, that we’ve got one more “bonus” bolt head marking to show you.
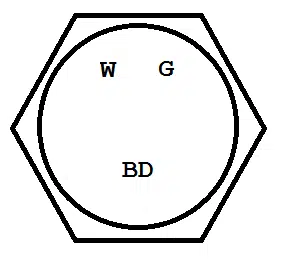
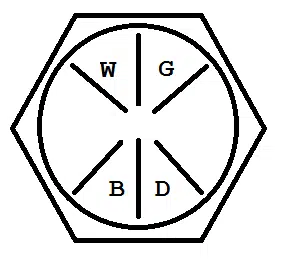
ASTM A354 Grade BD vs. SAE J429 Grade 8 Bolt Head Markings
Whoa! Are those Grade BD AND Grade 8 markings? That’s right — the mechanical properties of Grade BD are so close to SAE J429 Grade 8 that ASTM A354 allows you the option to include both grade identifiers if you wish. Therefore, the same fastener can qualify and be marked for both Grade BD and Grade 8. Of course, this begs the question: Why do ASTM Grade BD and SAE J429 Grade 8 both exist?
Well, SAE J429 only covers diameters up to 1 ½”, and ASTM A354 covers parts up to 4”. So ASTM A354 allows for larger fasteners to be covered in the same standard as smaller ones.
RELATED: Need a specialty bolt, screw, or stud? Wilson-Garner can help.
Learn More About Bolt Head Markings with Wilson-Garner
Interested in learning a bit more about bolt head markings? We give an overview of what bolt head markings mean and provide some more inch-series examples from SAE J429 in this blog. Or, we also talk about some metric head markings in this blog. Check them out.
And if you have any questions that these blogs can’t answer for you, feel free to reach out to us. With plenty of experience in the fastener industry, we’ll likely have an answer for you. Give us a call at (800) 656-2658 or contact us online.