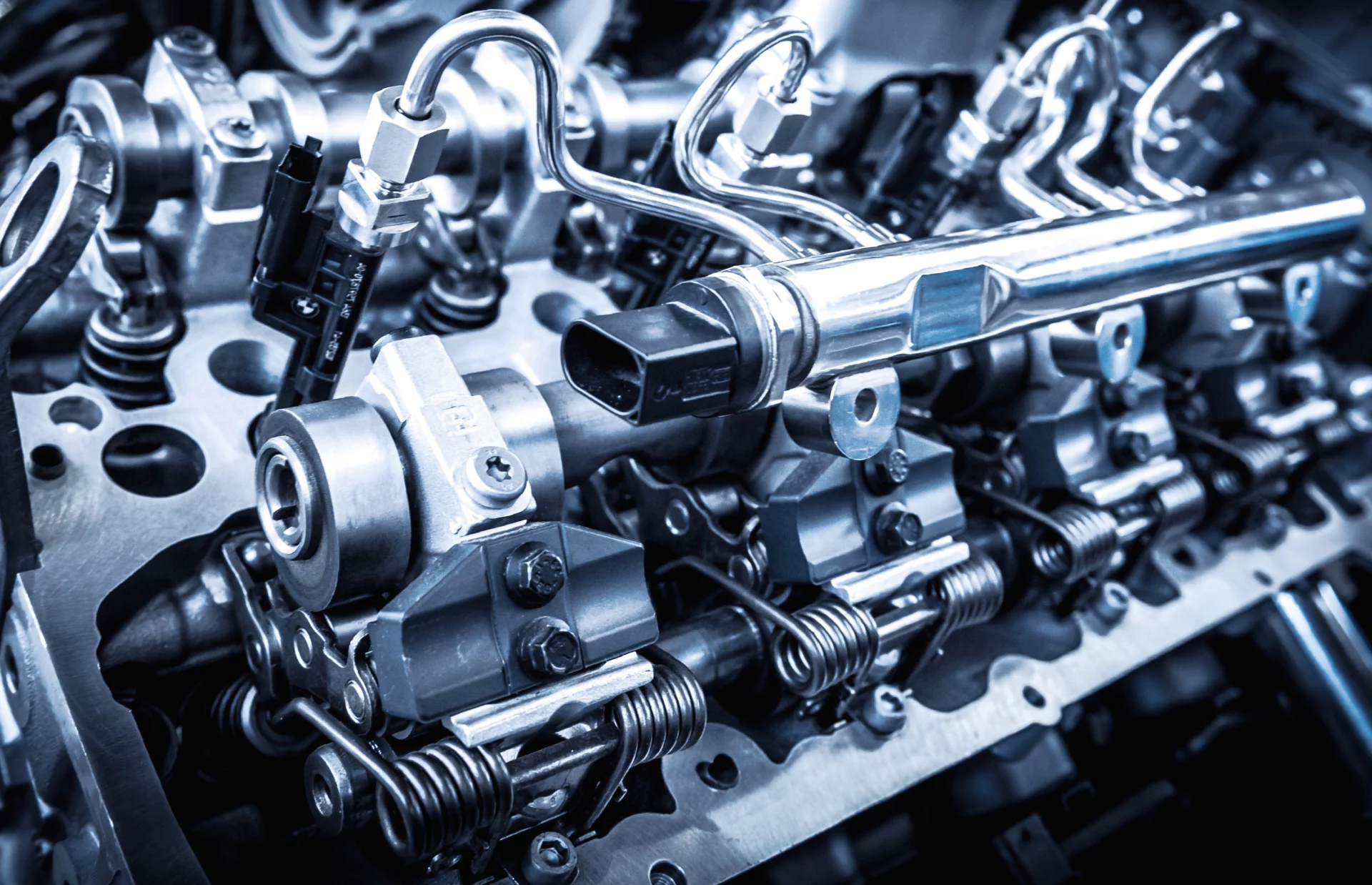
You might be shocked by the number of fasteners required to build an engine and keep it running properly. But these fasteners are critical to the engine’s performance, which is why it’s so important to purchase them from a trusted manufacturer. Not only do you need the right parts, but you need to factor in the quality and reliability of those parts as well.
Whether you’re shopping parts for cars, trucks, planes, etc., here’s some important information to know about engine fastener types, applications, and how to ensure you’re getting top quality.
What Are Engine Fasteners?
An engine fastener is any type of fastener used to keep a machine’s engine components intact and functioning properly.
That’s a pretty cut-and-dry definition, but it shouldn’t take away from the importance of these parts. Engine fasteners have a critical role in machine performance, and it often takes a lot of them to accomplish it with quality and consistency. In fact, some engines require over 100 fasteners to be installed.
Common Types of Engine Fasteners
As you can likely imagine, there are many types of fasteners used in engines. Here are three of the most common engine fastener categories, along with some more specific examples of each of them.
Engine Bolts
Bolts are externally threaded fasteners designed for insertion through holes in assembled parts. They’re typically intended to be tightened or released by torquing a nut. Some common types of bolts used in engines are:
- Engine mount bolts, which help hold the engine in place within the machine.
- Rod bolts, which are double-ended bolts that “stretch” when torque is applied. They’re used in many places throughout an engine and are known best for tolerating the force generated by moving pistons. Out of all engine fasteners, these are usually the ones that experience and can manage the most stress during operation.
- Head bolts, which keep the engine head gasket in place and secure cylinder heads. They can be exposed to quite a bit of mechanical pressure.
Engine Studs
Studs are externally threaded fasteners that look and operate as threaded bars. They’re usually used to join two parts with internally threaded holes together.
Within an engine, studs often act as guide pins and align components like gaskets, engine covers, and more. They’re also sometimes used in place of bolts (for the applications described above) when paired with nuts.
Engine Nuts
Nuts are internally threaded fasteners. They’re almost always used in conjunction with an externally threaded fastener to join multiple parts together.
Within an engine, nuts are paired with bolts and studs when a locking mechanism is necessary. However, they’re not always needed. Tapped holes, which have threads cut into the hole’s interior, are pretty common in engines. They’re used in metals where a nut and bolt combination can’t be used.
Important Engine Fastener Specifications
Engine fasteners often must be engineered to endure a great amount of force and stress. Therefore, they’re always required to meet certain specifications regarding fastener material, size, strength, etc. Specifications can vary tremendously based on your particular application, but these are some of the categories you’ll look for:
Material
Similar to other fasteners, engine fasteners are most commonly made from various types of steel. However, depending on specific use, they may also be made from aluminum, titanium, superalloys, and others.
Size
When you think about engine fastener size, you need to consider many different measurements, most importantly:
- Length
- Major diameter
- Minor diameter
- Pitch diameter
- Nominal diameter
- Thread pitch
These measurements are generally specified in a design blueprint for a specific part.
Not sure what any of these terms mean? Check out our Guide to Fastener Terminology.
Grade or Property Class
There are tons of fastener grades, or property classes, out there. They define various specifications for how a fastener must be made, like how strong it needs to be. Fastener strength is usually expressed in terms of low, medium, high, and really high strength requirements.
Here are those levels of strengths match up with some of the most common fastener grades. It’s important to note that there are lots of other fastener grades beyond what we have listed here. These are just some of the most common.
- Low strength: Grade 2 (inch) or Property Class 4.6 (metric)
- Medium strength: Grade 5 (inch) or Property Class 8.8 (metric)
- High strength: Grade 8 (inch) or Property Class 10.9 (metric)
- Really high strength: Property Class 12.9 (metric)
Tensile Strength
A fastener’s grade or property class (PC) requirement is what dictates its required tensile strength. Here’s a chart of what those may look like for different grades and property classes, both inch and metric. Again, these are just some of the most common grades — not the only ones.
| Grade/Property Class | Tensile Strength |
| Grade 2 or PC 4.6 | 58,000 psi or 400 MPa |
| Grade 4 or PC 8.8 | 116,000 – 120,000 psi or 800-830 MPa |
| Grade 8 or PC 10.9 | 150,800 psi or 1040 MPa |
| PC 12.9 | 1220 MPa |
Common Engine Fastener Applications
So when would you use engine fasteners? Well, for any application that requires an engine. But we’ll get a bit more specific than that. Here are the engine fastener applications and industries we deal with most here at Wilson-Garner.
- Automotive
- Heavy Machinery
- Heavy Truck
- Military
We work with a many original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) that request custom fasteners to test and manufacture new products — for instance, our automotive OEMs like Chrysler. They’ll send us the blueprint they need based on their vehicle engine’s design, and we’ll manufacture it just as intended.
For High-Quality Engine Fasteners, Trust Wilson-Garner.
Need an engine fastener manufacturer you can trust to get the job done right? Choose Wilson-Garner. You hand us a design blueprint for your part, then we’ll ensure it’s manufactured exactly to those specifications and to the highest level of quality — on time, all the time, every time.
For a high level of quality and confidence, start your project with us today. Give our team a call or contact us online.